

- TRANG CHỦ
- GIỚI THIỆU
- SẢN PHẨM
- Nguyên liệu ngành nhựa
- Hóa chất ngành Giấy
- Trợ bảo lưu và thoát nước
- Chất tăng bền ướt
- Chất phủ lô
- Hóa chất giặt chăn lưới
- Chất diệt khuẩn
- Tăng trắng huỳnh quang
- Lơ tím, xanh
- Trợ chống thấm bề mặt
- Phẩm màu cho giấy bao bì
- Phẩm màu cho giấy bìa màu
- Hóa chất cho giấy tráng phủ
- Chất phá bọt
- Chất tăng bền khô
- Hóa chất xử lý nước thải
- Chất phân tán Tissue
- Chất khử mực
- Hóa chất ngành sơn
- Nguyên liệu xi măng
- Hóa chất công nghiệp
- Hóa chất ngành dệt nhuộm
- TIN TỨC
- KỸ THUẬT
- KHÁCH HÀNG
- TUYỂN DỤNG
- LIÊN HỆ
DANH MỤC SẢN PHẨM
TÀI LIỆU KỸ THUẬT
- tdsp640j.pdf
- propertyanalysiswt45ancalpha.pdf
- tdspalmac1600alpha.pdf
- tdspalmac1500alpha.pdf
- stearicacid1838alpha.pdf
- coaofstearicacidr401860alpha.pdf
- deepwhiteabpxpowderalpha.pdf
- kymenẹ57htangbenuotvn.pdf
- prosofttq28881.pdf
- tdskymene705.pdf
- kymenẹ57htds.pdf
- hyt80tdsenalpha.pdf
- snowhite80tdsvietnam.pdf
- pmmacm207.pdf
- pc110uiso.pdf
- opticalbrighteningagent2plc.docx
- opticalbrighteningagent4plcvn.pdf
- melaminetdsalpha.pdf
- coazncl2alpha.jpg
- tdszncl2alpha.pdf
- pc1220ueng.pdf
- pc1100u.pdf
- pc1070ueng.pdf
- absag15átds.pdf
- ppk8009tdsen.pdf
- absterlurangp35.pdf
- absterlurangp22.pdf
- bakelit161jcoaalpha.pdf
- bakelit151jcoaalpha.pdf
- bakelit141jcoaalpha.pdf
- bakelit141coaalpha.pdf
- makrolonet3117isoen.pdf
- makrolonet3113isoen.pdf
- makrolonal2647isoen.pdf
- makrolon2807isoen.pdf
- makrolon2407isoen.pdf
- alphavncompanyprofile.pdf

- Bài viết

- Coagulation & Flocculation
Ngày đăng: 03/07/2013, 10:41 am
Lượt xem: 1003
Lượt xem: 1003
Coagulation:
Promoting the natural aggregation of fine particles during inter-particle collisions by enhancing naturally occurring, short range attractive forces between particles.
Typically coagulation aggregates particles in the 0.1 – 1 μm range to 1 – 10 μm. The aggregates formed are dense with minimal water entrained within the structure
Flocculation:
Bringing together small particles or aggregates into much larger aggregations using long chain molecules which bridge between particles and bind them into a macro-structure (floc).
Typically flocculation aggregates particles in the 1 – 10 μm range to 100 – 10,000 μm. The aggregates normally have a large quantities of water trapped within the macro-structure resulting in lower density particles
Coagulation Flocculation
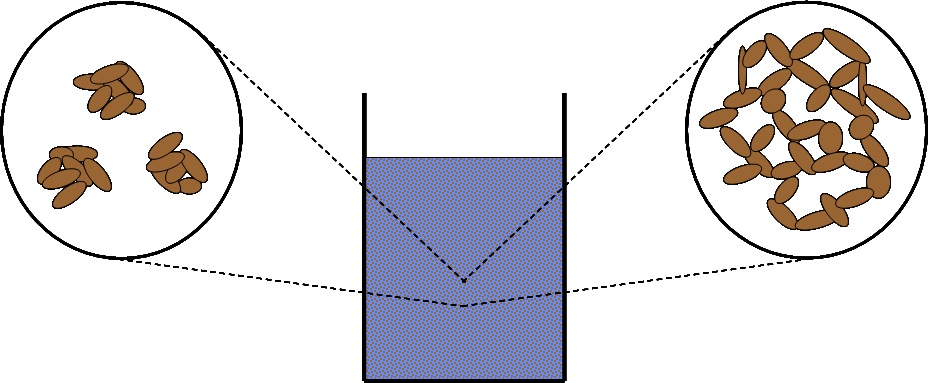
Coagulation Flocculation

Coagulation – Inorganic Products
Inorganic Coagulants:
Multi-valent metal ions
•Feric (iron) salts - sulphate & chloride
•Aluminium - sulphate (alum)
•Calcium - hydroxide (lime)
Tri-valent cations are general more effective due to higher charge
Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC)
•poly - aluminium & hydroxyl coordination complex
•activity quoted as % Al2O3 content
•degree of polymerisation - basicity (ratio of Al & (OH) groups
•normal basicity - 1.5 (50%)
•sulphate increases degree of polymerisation
Alternate Names:- Basic aluminium chloride
Aluminium hydroxy chloride
Aluminium chlorohydrate
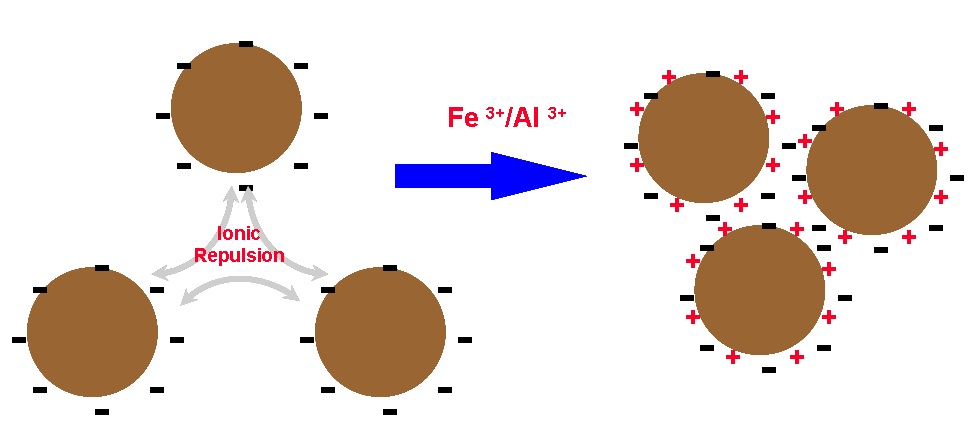
Dispersed Particles Coagulated Particles

Mechanism - Charge Neutralisation
Coagulation – Organic Polymers
Organic Coagulants
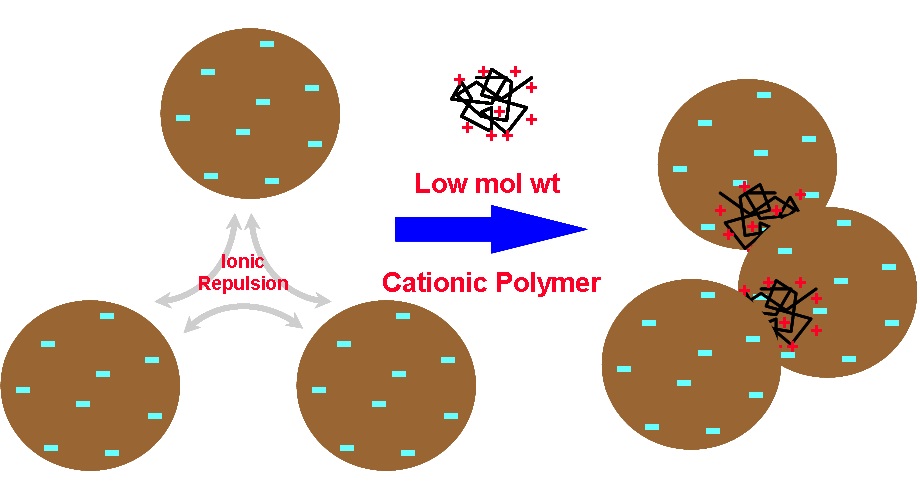
Low Molecular Weight Cationic Polymers
•polyamines
•polydadmacs
•mannichs
•polyacrylate ester quats (eg DMAEMA quat)
•formaldehyde-amine resins
Mol weight - typically 105 to 2 x 106
Physical Form - usually aqueous solutions
Dispersed Particles Coagulated Particles

Mechanism - Patch Coagulation
Flocculation Mechanisms
Flocculation:
The association of small particles or agglomerates
into large macro- structures (”flocs”) which either settle rapidly from suspension or are suitable for de-watering by mechanical means. (eg pressure filtration)The association of small particles or agglomerates
Complex Flocculation:
Coagulants and flocculants used in combination. The coagulant captures fine, well dispersed colloidal particles whilst the flocculant provides rapid separation from the aqueous suspension.
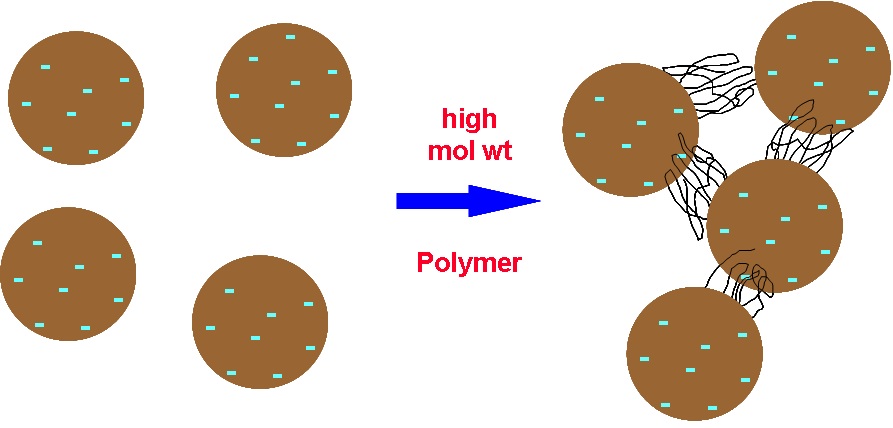
Flocculants:
High molecular weight (typically 5 - 20M) acrylic polymers, usually based on co-polymers of acrylamide. Both the molecular weight and charge density (positive or negative) may be varied to tailor the polymer to individual applications
Flocculation Mechanisms
Dispersed Particles Flocculated Particles
Dispersed Particles Flocculated Particles

Mechanism - Bridging Flocculation
Bài viết khác
HỖ TRỢ TRỰC TUYẾN
 Hotline: 0904 022 133
Hotline: 0904 022 133 Phòng KD hạt nhựa: 024.3776 7722/33, ext: 102; 103
Phòng KD hạt nhựa: 024.3776 7722/33, ext: 102; 103 Email: sales@alphachem.com.vn
Email: sales@alphachem.com.vn Phòng KD hóa chất: 024.3776 7722/33, ext: 104; 105
Phòng KD hóa chất: 024.3776 7722/33, ext: 104; 105 Email: sales@alphachem.com.vn
Email: sales@alphachem.com.vn Fax: +8424.37767744
Fax: +8424.37767744 Email:
Email:- Facebook Hóa Chất Alpha
-
 binh.alpha
binh.alpha
TÌM KIẾM NÂNG CAO
NHẬN TIN SẢN PHẨM MỚI
HOẠT ĐỘNG
- Thông báo nghỉ Tết Nguyên Đán Canh Tý 2019
- Tuyển Trưởng phòng kinh doanh hạt nhựa kỹ thuật - Business Manager
- Tuyển dụng Trưởng phòng kinh doanh/Nhân viên kinh doanh hóa chất, hạt nhựa
- Tuyển Nhân viên kinh doanh hóa chất
- Tuyển nhân viên kinh doanh hóa chất, hạt nhựa
- Thay đổi tên công ty và địa chỉ văn phòng
- Đoàn Hiệp hội Giấy Việt Nam tham dự FAPPI 31 tại Indonesia
- Công ty cổ phần giấy việt trì 50 năm xây dựng và phát triển
- Công ty CP giấy Việt Trì tự hào với truyền thống 50 năm xây dựng và phát triển
- Triển lãm China International Water Chem Exhibition 2013 lần thứ 9
LIÊN KẾT WEBSITE
- Công ty Cổ phần XNK Bắc Giang (Nhà máy Giấy Xương Giang)
- Công ty Cổ phần DEVYT (Nhà máy Giấy BBP)
- Công ty Cổ phần Giấy An Hòa
- Công ty Cổ phần Giấy Bao bì Đồng Tiến
- Công ty Giấy Tissue Sông Đuống
- Công ty TNHH Xưởng Giấy Chánh Dương
- Tập đoàn Giấy Tân Mai
- Công ty TNHH Giấy Trường Xuân
- Công ty TNHH Giấy Kraft Vina
- Công ty Giấy Hải Phòng
- Tổng công ty Giấy Việt Nam (Nhà máy Giấy Bãi Bằng)
- Công ty Cổ phần Giấy Việt Trì
- Trang Web Danh bạ các công ty hóa chất
- Công ty Cổ phần Giấy Sài Gòn
- Công ty cổ phần Sản xuất và thương mại P.P
- Công ty cổ phần Giấy Vạn Điểm
- Thời báo kinh tế - Diễn đàn Doanh Nghiệp Việt Nam
- Giấy – Wikipedia tiếng Việt
- Hiệp hội giấy và bột giấy Việt Nam (VPPA)
- Tin tuc 24h | tin nhanh bong da | the thao | thoi trang, giai tri vn
- Báo Dân trí – Thông tin mọi lúc, mọi nơi tới mọi người, mọi nhà
- Tin nhanh VnExpress - Đọc báo, tin tức online 24h
LƯỢT TRUY CẬP
- Đang xem
- Hôm nay 813
- Tổng lượt truy cập 4,084,096
THÔNG TIN TIỆN ÍCH
BÀI VIẾT MỚI NHẤT
- Tuyển dụng Trưởng phòng kinh doanh/Nhân viên kinh doanh Hóa chất, Hạt nhựa
- PAC và ứng dụng trong xử lý nước
- Cần tuyển nhân viên kinh doanh hóa chất, nhựa
- Tuyển 01 lái xe văn phòng
- Xử lý nước thải sản xuất giấy
- Lịch sử sản xuất giấy
- Các chất phụ gia trong ngành giấy
- List of Customers
- Nhựa thông trong kỹ thuật gia keo bề mặt cho giấy
- Nguyên nhân và cơ chế của hiện tượng bóc sợi
- Các bệnh giấy thường gặp và cách khắc phục
- Keo chống thấm AKD
- Chất độn cho giấy
- Nhuộm màu cho Giấy
- Khách hàng
- 6-8/6/2013: Triển lãm Quốc tế về ngành Giấy và Bột giấy Việt Nam
- Chất trợ bảo lưu Percol 182
- Tuyển 01 nhân viên kinh doanh hóa chất











Bình luận
Chưa có bình luận nào!
Phản hồi
Bình luận từ Facebook